Selected Publications
Accurate Prediction of Aqueous Free Solvation Energies Using 3D Atomic Feature-Based Graph Neural Network with Transfer Learning
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2022-04-21
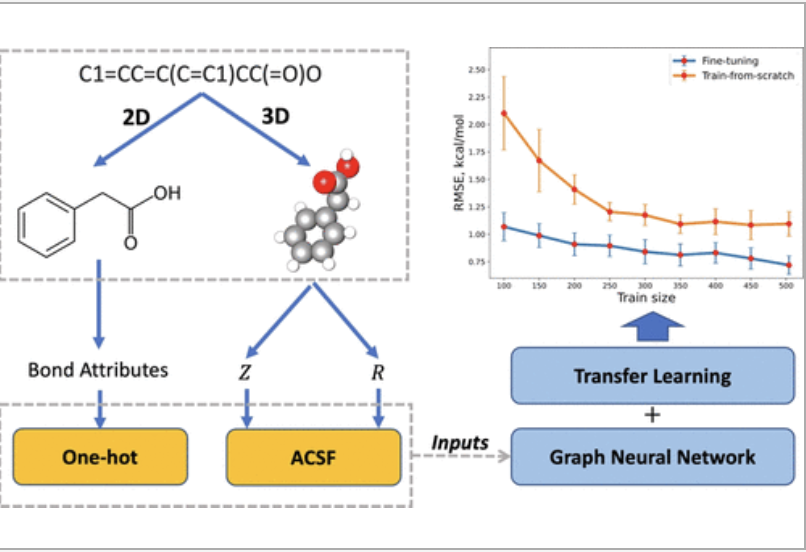
Abstract
we first build a large and diverse calculated data set Frag20-Aqsol-100K of aqueous solvation free energy with reasonable computational cost and accuracy via electronic structure calculations with continuum solvent models. Then, we develop a novel 3D atomic feature-based GNN model with the principal neighborhood aggregation (PNAConv) and demonstrate that 3D atomic features obtained from molecular mechanics-optimized geometries can significantly improve the learning power of GNN models in predicting calculated solvation free energies. Finally, we employ a transfer learning strategy by pre-training our DL model on Frag20-Aqsol-100K and fine-tuning it on the small experimental data set, and the fine-tuned model A3D-PNAConv-FT achieves the state-of-the-art prediction on the FreeSolv data set with a root-mean-squared error of 0.719 kcal/mol and a mean-absolute error of 0.417 kcal/mol using random data splits.
Multitask Deep Ensemble Prediction of Molecular Energetics in Solution: From Quantum Mechanics to Experimental Properties
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2023-01-06
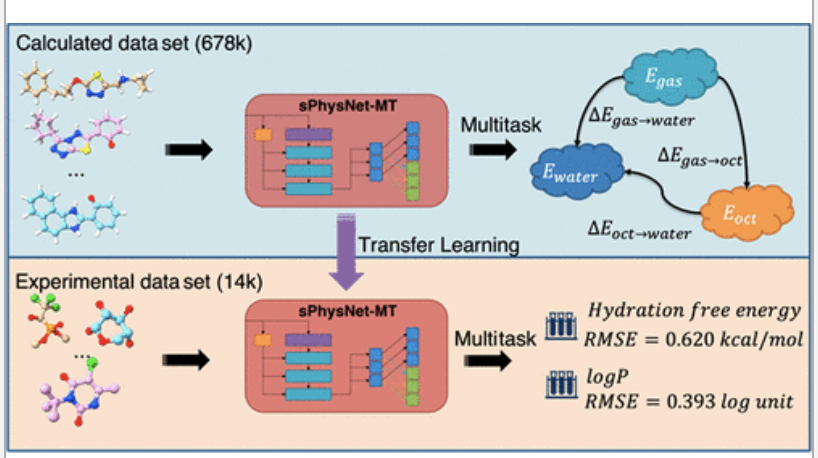
Abstract
In this work, we present a multitask deep ensemble model, sPhysNet-MT-ens5, which can simultaneously and accurately predict electronic energies of molecules in gas, water, and octanol phases, as well as transfer free energies at both calculated and experimental levels. On the calculated data set Frag20-solv-678k, which is developed in this work and contains 678,916 molecular conformations, up to 20 heavy atoms, and their properties calculated at B3LYP/6-31G* level of theory with continuum solvent models, sPhysNet-MT-ens5 predicts density functional theory (DFT)-level electronic energies directly from force field-optimized geometry within chemical accuracy. On the experimental data sets, sPhysNet-MT-ens5 achieves state-of-the-art performances, which predict both experimental hydration free energy with a RMSE of 0.620 kcal/mol on the FreeSolv data set and experimental logP with a RMSE of 0.393 on the PHYSPROP data set. Furthermore, sPhysNet-MT-ens5 also provides a reasonable estimation of model uncertainty which shows correlations with prediction error. Finally, by analyzing the atomic contributions of its predictions, we find that the developed deep learning model is aware of the chemical environment of each atom by assigning reasonable atomic contributions consistent with our chemical knowledge.
The study on the electron transfer between cytochrome c and single-walled carbon nanotube – The calculations of the reorganization free energy, the coupling matrix element and the rate constant
Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2024-06-04

Abstract
We have studied the electron transfer (ET) reaction between the cytochrome c (Cyt c) and the single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT). The ET reorganization energy, the ET coupling matrix element and the ET rate constant for Cyt c-SWCNT system have been calculated using QM + MM and the pathway tunneling model based on semi-classical Marcus theory.
Accurate Prediction of NMR Chemical Shifts: Integrating DFT Calculations with Three-Dimensional Graph Neural Networks
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2024-06-06
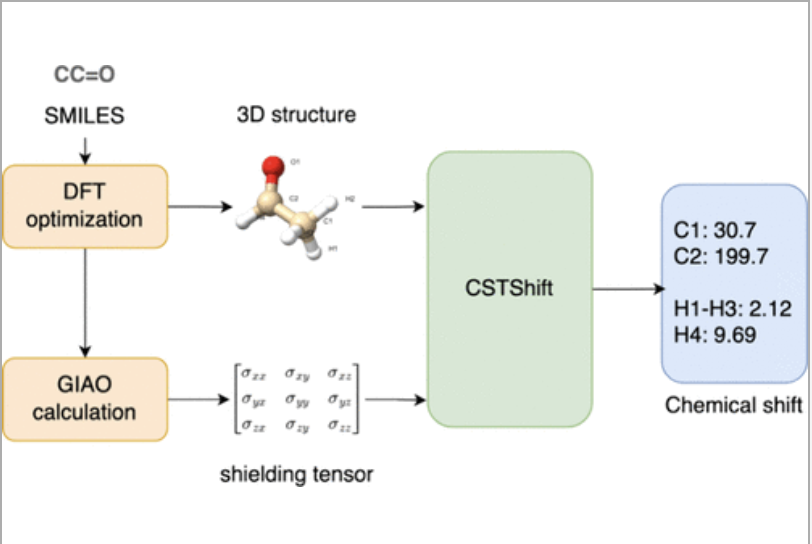
Abstract
This study presents a new 3D GNN model to predict 1H and 13C chemical shifts, CSTShift, that combines atomic features with DFT-calculated shielding tensor descriptors, capturing both isotropic and anisotropic shielding effects. Utilizing the NMRShiftDB2 data set and conducting DFT optimization and GIAO calculations at the B3LYP/6-31G(d) level, we prepared the NMRShiftDB2-DFT data set of high-quality 3D structures and shielding tensors with corresponding experimentally measured 1H and 13C chemical shifts. The developed CSTShift models achieve the state-of-the-art prediction performance on both the NMRShiftDB2-DFT test data set and external CHESHIRE data set. Further case studies on identifying correct structures from two groups of constitutional isomers show its capability for structure assignment and elucidation.
